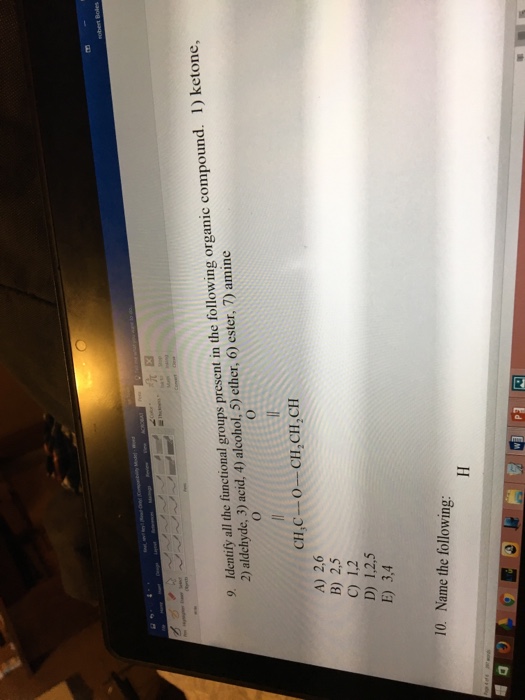
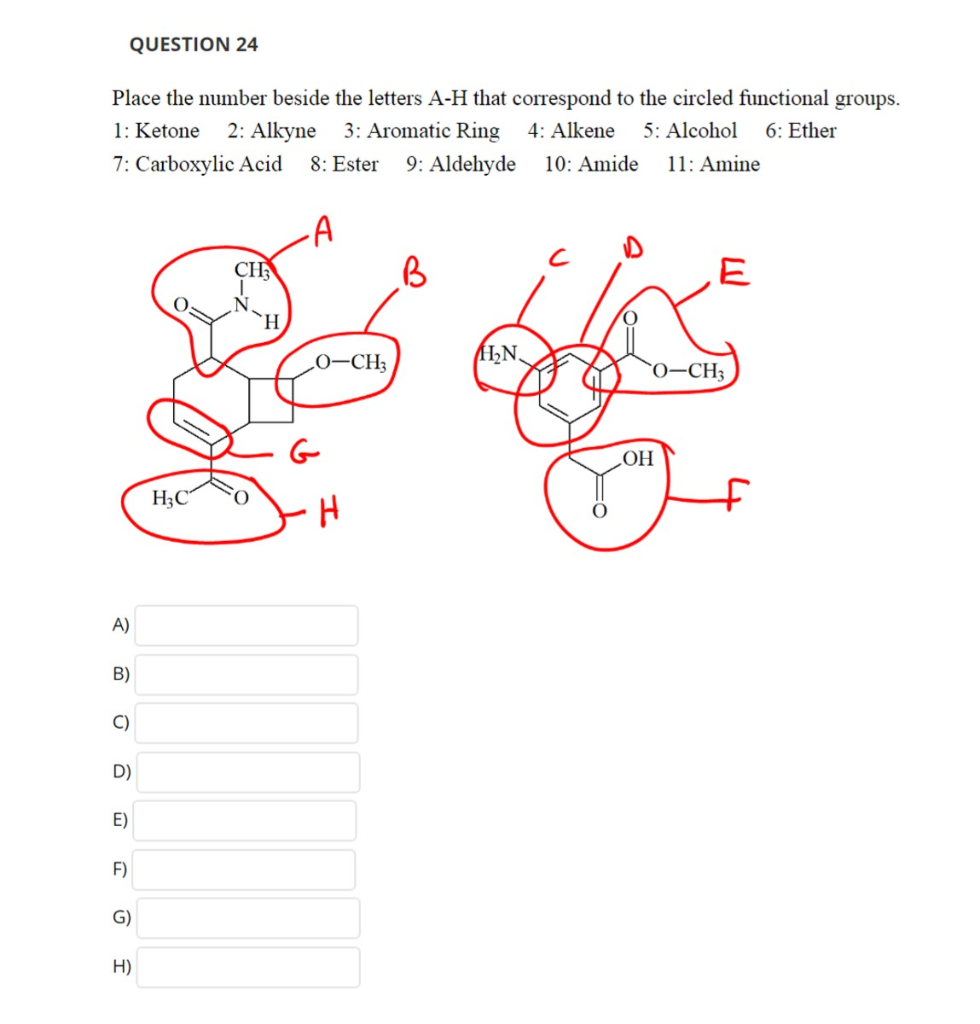
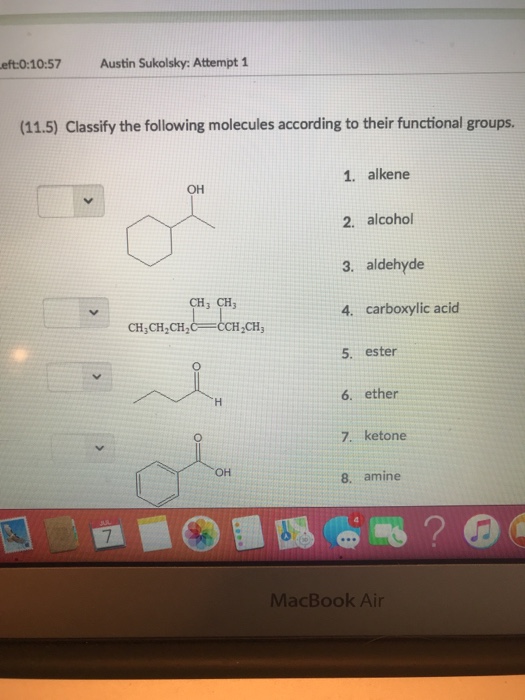
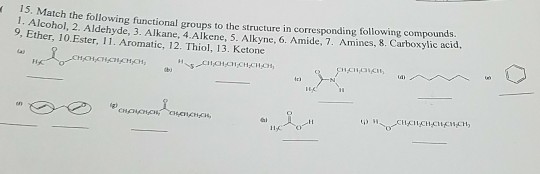
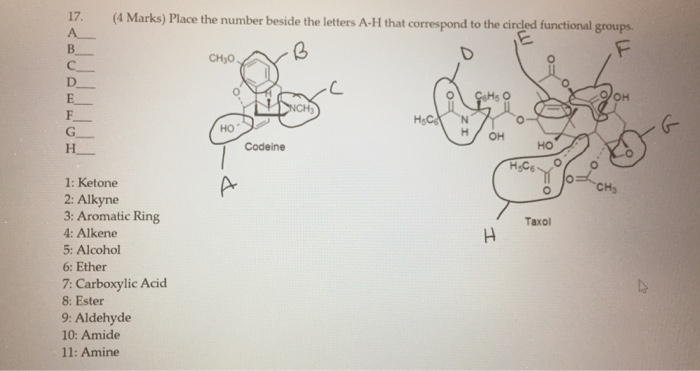
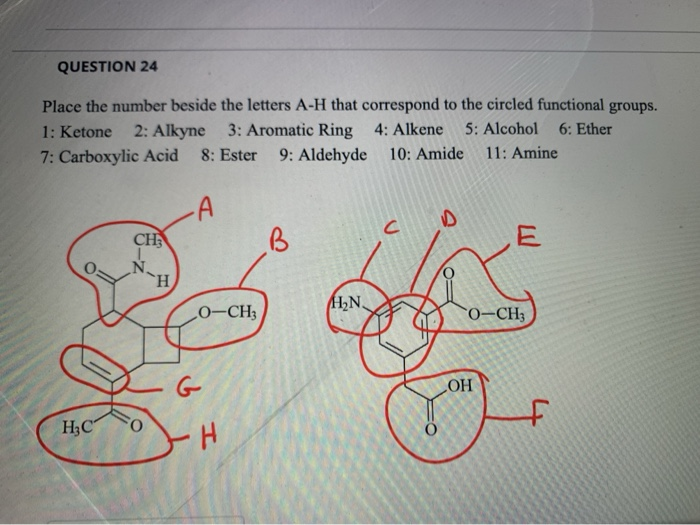
1 Ketone 2 Aldehyde 3 Acid 4 Alcohol 5 Ether 6 Ester 7 Amine

B an ion with molecular formula c 3 h 5 o 6 p 2 that includes aldehyde secondary alcohol and phosphate functional groups.
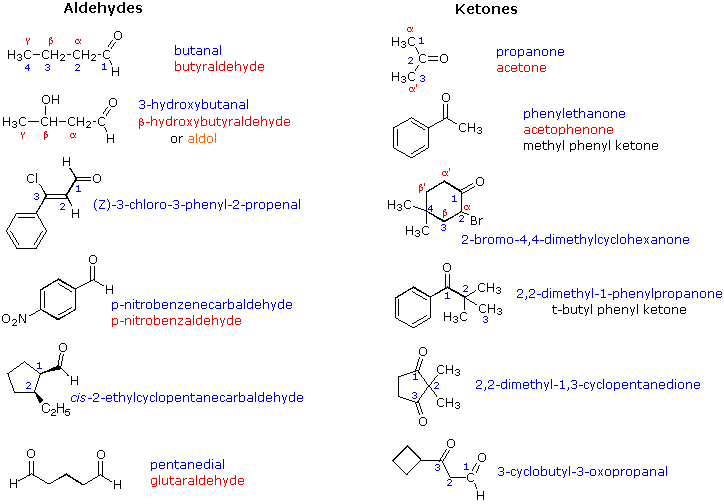
1 ketone 2 aldehyde 3 acid 4 alcohol 5 ether 6 ester 7 amine. Describe the structure of molecules that belong to the alcohol ether thiol sulfide disulfide aldehyde and ketone families and describe how they are named. For example h 2 c o is methanal more commonly called formaldehyde since an aldehyde carbonyl group must always lie at the end of a carbon chain it is always is given the 1 location position in numbering and it is not necessary to include it in the name. The carbon atom exhibits sp 2 hybridization. As text an aldehyde group is represented as cho.
1 a primary alcohol 2 an aldehyde 3 a ketone 4 a secondary alcohol 28. A ketone is represented as c o or co. Stem names of aldehydes and ketones are derived from those of the parent alkanes using an al ending for an aldehydes and an one ending for a ketone. Describe the nucleophilic substitution reactions that can be used to prepare alcohols ethers thiols and sulfides.
And so this part would be named 6 fluoro 3 phenyl heptan 1 ol. Hso chc ch b then b is 1 acetone 2 trichloroacetone 3 acetaldehyde 4 chloral 29. The iupac system of nomenclature assigns a characteristic suffix al to aldehydes. In both aldehydes and ketones the geometry around the carbon atom in the carbonyl group is trigonal planar.
4 20 4 3 60 hgso. Aldehydes 17 ketones 19 esters 24 amides 30 nitriles 25 h 3c ch 3 c o ho h 3cn ch 3 2 c o h 3ccn acidity of 1 3 dicarbonyl compounds h 3coch3 c o hcch. Typical pk a s of carbonyl compounds α protons. Esters are produced by the reaction of acids with alcohols.
Firstly it is a 7 carbon chain with a hydroxyl group on the end meaning that is a heptan 1 ol. We prepare carboxylic acids by the oxidation of aldehydes or alcohols whose oh functional group is located on the carbon atom at the end of the chain of carbon atoms in the alcohol. The α protons of esters are less acidic that ketones and aldehydes. A a compound with molecular formula c 6 h 11 no that includes alkene secondary amine and primary alcohol functional groups.
Distinguish 1 2 and 3 alcohols. Together they form 7 3 chlorobutoxy 6 fluoro 3 phenyl heptan 1 ol. The common names of ketones like those of ethers consist of the names of the groups attached to the carbonyl group followed by the word ketone. Ester α hydrogens and their pk a s.
Two of the sp 2 orbitals on the carbon atom in the carbonyl group are used to form σ bonds to the other carbon or hydrogen atoms in a.